Article published on the ASSET website
High rates of vaccination coverage in childhood are main indicators for public health. However, reaching and maintaining such a target is not always an easy task for public health institutions, and the spread of vaccine refusal and hesitancy is making this even harder.
Enforcing mandatory vaccinations is one of the strategies that some countries adopted and others are considering in order to face this issue. Depending on local legislations, legal consequences for those who do not accept the uptake can be very different, ranging from pecuniary penalties to hurdles to attend public schools. In some cases, parents may even incur penal consequences, as it recently happened in France, were two parents refusing to vaccinate their children risked a jail sentence. Nevertheless, the efficacy of such an approach has been questioned.
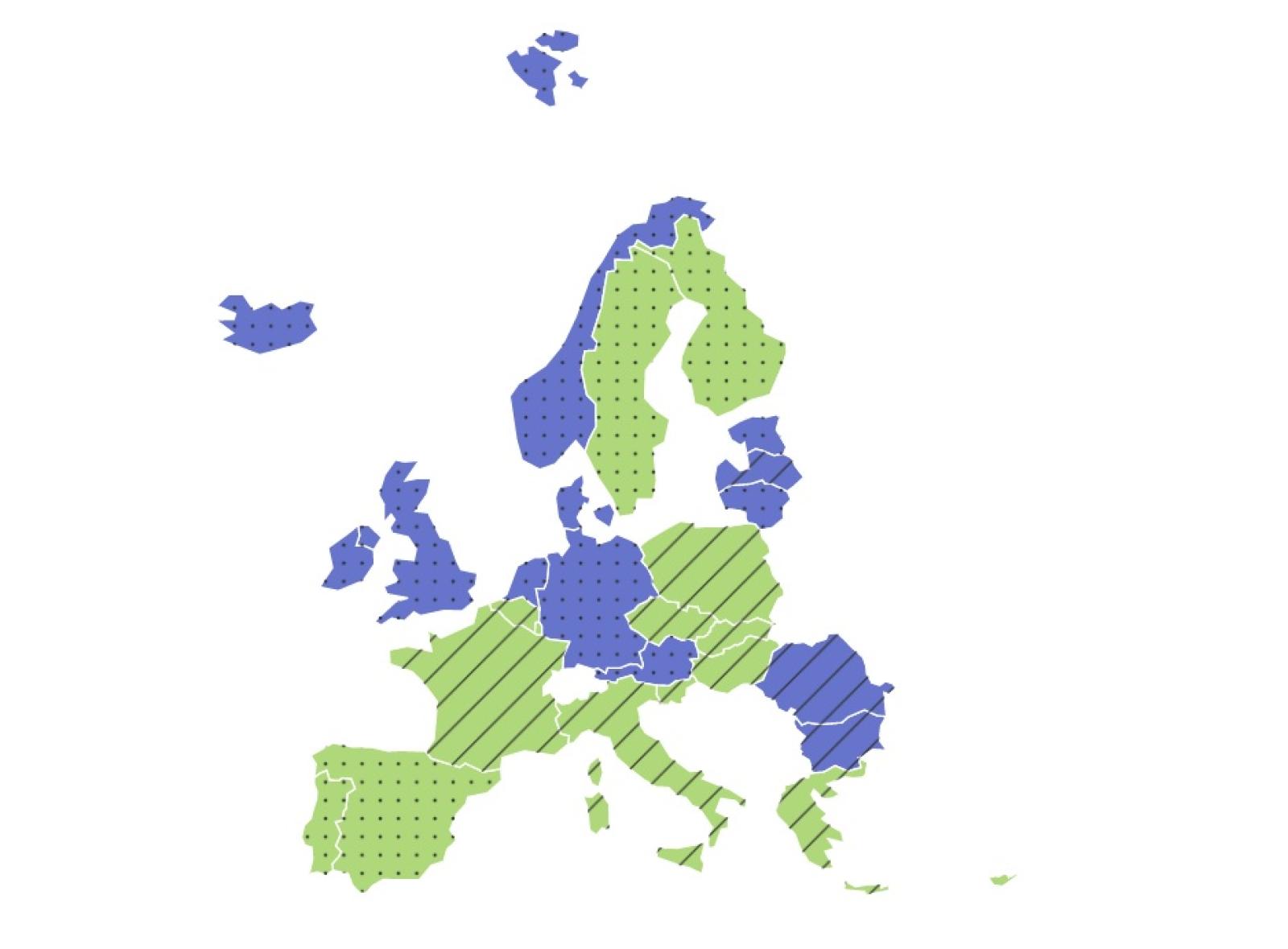
ASSET performed an analysis on the issue, comparing coverage rates of immunisation against polio (Pol3), measles (MCV1) and pertussis containing vaccines (DTP3)* in European Union/European Economic Area (EU/EEA) countries, where, according to different policies, these vaccinations are either mandatory or recommended.
This comparison cannot confirm any relationship between mandatory vaccination and rates of childhood immunization in the EU/EEA countries.
* In some countries, such as Italy, vaccination against pertussis is highly recommended but not compulsory, while those against diphteria and tetanus on the contrary are, but the three are usually administered in one single shot.